1. Introduction to BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor)
The Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) is a three-layer, three-terminal semiconductor device capable of amplifying or switching electrical signals.
It was invented in 1947 at Bell Labs and has since been a cornerstone of analog electronics.
The term “bipolar” refers to the fact that both electrons and holes (two types of charge carriers) are involved in current conduction.
🔹 Definition:
A BJT is a current-controlled device where a small current at the Base terminal controls a larger current between the Emitter and Collector.
2. Structure of BJT
The BJT consists of three regions:
| Region | Function |
|---|---|
| Emitter (E) | Heavily doped to inject carriers |
| Base (B) | Very thin and lightly doped to pass carriers |
| Collector (C) | Moderately doped to collect carriers |
There are two types of BJTs based on the arrangement of these regions:
- NPN transistor
- PNP transistor
🎨 Diagram: BJT Structure
➡️ NPN Transistor Structure:
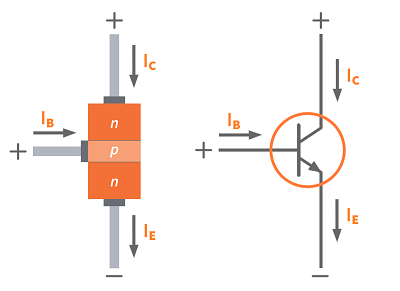
🎨 Symbol of BJT
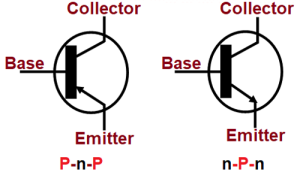
🎨 Symbols:
| NPN Transistor | PNP Transistor |
|---|---|
| The emitter arrow points inward | Emitter arrow points inward |
4. Working Principle of BJT
When a small base current (Ib) is applied:
- It controls a much larger current flowing from Collector (Ic) to Emitter (Ie).
Mathematically:
IE=IB+IC
5. Modes of Operation
BJTs can operate in four modes:
| Mode | Base-Emitter | Base-Collector | Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cutoff | Reverse biased | Reverse biased | OFF state (open switch) |
| Active | Forward biased | Reverse biased | Amplification |
| Saturation | Forward biased | Forward biased | ON state (closed switch) |
| Reverse Active | Reverse biased | Forward biased | Rarely used |
6. Types of BJT
🔵 NPN Transistor:
- Electrons are majority carriers.
- Easier to fabricate.
- Used for positive voltages.
🔵 PNP Transistor:
- Holes are majority carriers.
- Operates with negative voltages.
Comparison Table:
| Feature | NPN | PNP |
|---|---|---|
| Major Carrier | Electrons | Holes |
| Biasing | Positive voltage to base | Negative voltage to base |
| Current Direction | Collector to emitter | Emitter to collector |
7. Characteristics of BJT
| Parameter | Typical Values |
|---|---|
| Current Gain (β) | 20–1000 |
| Cut-off Voltage (Vbe) | 0.6V–0.7V (Si), 0.2V (Ge) |
| Maximum Collector Current (Ic) | 10mA – 100A |
| Power Dissipation | 100mW – 500W |
| Frequency Response (fT) | Up to 300GHz |
8. Applications of BJT
✅ Amplifiers — Audio systems, RF communication.
✅ Switching Circuits — Logic gates, relay drivers.
✅ Oscillators — Signal generation.
✅ Voltage Regulation — Power supplies.
✅ Motor Control — Robotics, drones.
| Application | Device Example |
|---|---|
| Audio Amplifiers | 2N3055 BJT |
| RF Circuits | BF199 BJT |
| Microcontrollers I/O Switching | BC547 NPN BJT |
9. Advantages of BJTs
- High gain and linearity.
- Reliable and robust.
- Good low-frequency performance.
- Easily available and inexpensive.
10. Limitations of BJTs
- Lower input impedance compared to FETs.
- More power dissipation.
- Slower switching speed than MOSFETs.
11. Modern Advances in BJTs (2025)
- SiC BJTs now available for high-temperature and high-voltage applications.
- Heterojunction Bipolar Transistors (HBTs) used for high-frequency 5G and satellite communication.
- Organic BJTs researched for flexible electronics.
12. FAQs: BJT
❓ Why is BJT called bipolar?
Because both electrons and holes are involved in current conduction.
❓ Which BJT is more common: NPN or PNP?
NPN BJTs are more common because electron mobility is higher than hole mobility, making them more efficient.
❓ What happens if the base current is zero?
The transistor stays OFF — no current flows from Collector to Emitter (cutoff region).
❓ Why is the base made very thin?
A thin base region increases current gain by minimizing the recombination of carriers.
13. Conclusion
The Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) remains a fundamental building block of electronic circuits despite the emerging technologies of MOSFETs and IGBTs.
BJTs’ simplicity, amplification capabilities, and robust performance ensure that they are still widely used across industries ranging from audio systems to aerospace.
As technology evolves, SiC BJTs and heterojunction devices are expanding the horizons of where and how BJTs are applied in the modern world.
